Due to rise in global demand of metals like Steel and Copper, the shift of metal used for coins was evident from 2004 when RBI started issuing coins in Ferratic Stainless Steel [FSS] instead of Copper-Nickel and later using Nickel-Brass alloy from 2009. The variations in alloy used was an essential step to keep the value of alloy lesser than the face value of coin and to curb the production value.
As a coin collector, I feel that no matter what the economic circumstances are, due to the shift of alloy from Copper-Nickel to other later alloys, the artistry of the coins diminished. Rather, I would say the attractiveness and beauty of coin artistry got diminished in FSS and Ni-Br coins.
Hence I personally like the coins released in Nickel and Copper-Nickel alloy.
Below are the 5 Rs. coins released by RBI.
5 Rupees: 1985 - 2005
Indira Gandhi - 1985

Year: 1985
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 12.6 g
Diameter: 31.1 mm
Thickness: 2.3 mm
Commemorative issue: Death of Indira Gandhi - Statesperson, 1917-1984
Obverse: Asoka Lion pedestal and the denomination below it.
Reverse: Bust of Indira Gandhi facing right.
Apart from this coin, 3 other coins were issued in her commemoration, the 50 paise coin was issued for general circulation and the 20 rupees and the 100 rupees coins were issued as proof coins.
The interesting thing about this coin is 'Its size'. This coin was unusually big for its denomination as compared to the other circulating coins then in India. Its big size caught attention of many people that time and continued to be the fancy of indian people there after. Below is the picture shows the comparative sizes of this coin and currently circulating 5Rs. coin.

 |
| Indira Gandhi |
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was the third Prime Minister of India and a central figure in Indian politics during the second half of the 20th century. She was elected a record four terms as Prime Minister from 1966–77 and again from 1980 until her assassination in 1984.Indira Gandhi was the only child of Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru.She was elected as a Congress President in 1959, inspite of this she refused to become prime minister in succession of her father and Mr.Lal Bahadur Shastri became Prime Minister of India. However, She finally took the batton of Prime Ministership after the mysterious death of Mr. Shastri in Russsia in 1966.
Click here to know more about Indira Gandhi.
===XXX===
Jawaharlal Nehru Centenary - 1989

Year: 1989
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 12.6 g
Diameter: 31.1 mm
Thickness: 2.3 mm
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 12.6 g
Diameter: 31.1 mm
Thickness: 2.3 mm
Commemorative issue: 100 Years of Birth of Jawaharlal Nehru.
Obverse: Asoka Lion pedestal and the denomination below it.
Reverse: Bust of Mr. Nehru facing right.
Apart from this coin, there were 3 other coins issued in his commemoration, 1 Rupee coin for general circulation and 20, 100 rupees coins were issued as proof and uncirculated specimens.
This was the 2nd big size coin after that of Indira Gandhi issued in 1985. This coin too is unusually bigger than the current 5 Rs. coins in circulation.

 |
| 1st Prime Minister of India |
Jawaharlal
Nehru (14 November 1889 – 27 May 1964), often referred to as Panditji,
was a leader in the Indian independence movement, and the first
independent Prime Minister of India.
Jawaharlal Nehru enjoyed an iconic status in India and was widely admired across the world for his idealism and statesmanship. His birthday, 14 November, is celebrated in India as Baal Divas ("Children's Day") in recognition of his lifelong passion and work for the welfare, education and development of children and young people. Children across India remember him as Chacha Nehru (Uncle Nehru). Hence to commemorate him, this coin was issued on 14 November 1964.
He is praised for creating a system providing universal primary education, reaching children in the farthest corners of rural India. Nehru's education policy is also credited for the development of world-class educational institutions such as the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Indian Institutes of Technology and the Indian Institutes of Management.
Jawaharlal Nehru enjoyed an iconic status in India and was widely admired across the world for his idealism and statesmanship. His birthday, 14 November, is celebrated in India as Baal Divas ("Children's Day") in recognition of his lifelong passion and work for the welfare, education and development of children and young people. Children across India remember him as Chacha Nehru (Uncle Nehru). Hence to commemorate him, this coin was issued on 14 November 1964.
He is praised for creating a system providing universal primary education, reaching children in the farthest corners of rural India. Nehru's education policy is also credited for the development of world-class educational institutions such as the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Indian Institutes of Technology and the Indian Institutes of Management.
Click here to know more about Jawaharlal Nehru.
===XXX===
World Of Work (ILO) - 1994

Year: 1994
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 8.9 gm
Diameter: 23.3 mm
Thickness: 2.6 mm
Commemorative issue: World of Work - 75 Years of International Labour Organization (ILO).
Obverse: Asoka Lion pedestal and the denomination value below it.
Reverse: Symbol of the International Labour Organization .
In commemoration of the 75th anniversary of I.L.O., India issued this 5 rupees coin on 27th October,1994. The other coins issued in the denomination of 50 rupees and 100 rupees, were only issued as proof and uncirculated specimens.
 |
| Logo of ILO |
The ILO is the international organization responsible for drawing up and overseeing international labour standards. It is the only 'tripartite' United Nations agency that brings together representatives of governments, employers and workers to jointly shape policies and programmes promoting Decent Work for all. This unique arrangement gives the ILO an edge in incorporating 'real world' knowledge about employment and work.
In 1969, the organization received the Nobel Peace Prize for improving peace among classes, pursuing justice for workers, and providing technical assistance to developing nations.
In 1969, the organization received the Nobel Peace Prize for improving peace among classes, pursuing justice for workers, and providing technical assistance to developing nations.
The I.L.O. has its headquarters at Geneva(Switzerland).lmost all (185 out of 193) UN members are part of the ILO including India.
Click here to know more about ILO.
===XXX===
50th Anniversary of UN - 1995

Year: 1995
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 9.18 gm
Diameter: 23 mm
Thickness: 2.9 mm
Commemorative issue: 50 Years - United Nations
Obverse: Asoka Lion pedestal and denomination below it.
Reverse: 50th year (1995) above UN logo with artistic number 50.
Reverse: 50th year (1995) above UN logo with artistic number 50.
The League of Nations failed to prevent World War II (1939–1945). Because of the widespread recognition that humankind could not afford a third world war, the United Nations was established to replace the flawed League of Nations in 1945 in order to maintain international peace and promote cooperation in solving international economic, social and humanitarian problems.
The United Nations Headquarters resides in international territory in New York City, with further main offices at Geneva, Nairobi, and Vienna. The organization is financed from assessed and voluntary contributions from its member states, and has six official languages: Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish.
Click here to know more about UN.
===XXX===
50 Years of FAO - 1995

Year: 1995
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 9 gm
Diameter: 23 mm
Thickness: 3 mm
Commemorative issue: 50 Years of FAO.
Obverse: Asoka Lion pedestal and denomination below.
Reverse: FAO symbol on hand clutching stalks of wheat.
Reverse: FAO symbol on hand clutching stalks of wheat.
All the details are same as that of 50 paise and 1 rupee coins of FAO.
===XXX===
8th Tamil World Conference (Saint Thiruvalluvar) - 1995

Year: 1995
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 9.13 gm
Diameter: 23 mm
Thickness: 2.94 mm
Commemorative issue: 8th World Tamil Conference.
Obverse: Asoka Lion pedestal with denomination below.
Reverse: Seated St. Thiruvalluvar.
Reverse: Seated St. Thiruvalluvar.
Thiruvalluvar was a celebrated Tamil poet and philosopher whose contribution to Tamil literature is the Thirukkural, a work on ethics. Thiruvalluvar is thought to have lived sometime between the 2nd century BC and the 8th century AD. This estimate is based on linguistic analysis of his writings, as there is no archaeological evidence for when he lived. He is sometimes also called Theiva Pulavar ("Divine Poet").

There is a 133-foot tall statue of Thiruvalluvar erected at Kanyakumari at the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent, where the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Indian Ocean converge. The 133 feet denote Tirukkural's 133 Chapters or athikarams and the show of three fingers denote the three themes Aram, Porul, and Inbam, i.e. the sections on Morals, Wealth and Love. The statue was designed by V. Ganapati Sthapati, a temple architect from Tamil Nadu.
Click here to know more about Saint Thiruvalluvar.
===XXX===
2nd International Crop Science Congress - 1996

Year: 1996
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 9 gm
Diameter: 23 mm
Commemorative issue: 2nd International Crop Science Congress.
Obverse: Ashoka Lion pedestal and the denomination below.
Reverse: The globe with crop all over it, encircled by “two ears of corn” on the bottom and a “double helix structure of DNA inside the gene” on the top. The inscription “Dwitiya Antarashtriya Fashal Vigyan Congress” in Hindi is shown at the left half and “2ND INTERNATIONAL CROP SCIENCE CONGRESS” in English is shown at the right half of the periphery.
The International Crop Science Society fosters communication among crop scientists. It organizes the International Crop Science Congress held every four years at various locations around the world. The first (1992) was held at Ames, Iowa. The motive behind these Congresses is to stimulate thinking among scientists as to how advances in crop science in all their aspects can assist in meeting the critical diverse global challenges that lie ahead. The second International Crop Science Congress was held at New Delhi (India) from 17th to 24th November,1996.
In commemoration of the 2nd International Crop Science Congress held at New Delhi, India issued this 5 rupees coin in November, 1996.
Disclaimer: This coin is one of the rarest coins issued by India and I don't have this coin in my collection.
===XXX===
Mother's Health is Child's Health - 1996

Year: 1996
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 8.97 gm
Diameter: 23 mm
Thickness: 2.85 mm
Commemorative issue: Mother's Health is Child's Health.
Obverse: Asoka Lion pedestal and the denomination below.
Reverse: Mother and Child within triangle.
Children who are malnourished have lowered resistance to infection and are more likely to die from common childhood ailments such as diarrhoeal diseases and respiratory infections. Those who survive may be locked into a vicious cycle of recurring sickness and faltering growth, often with irreversible damage to their cognitive and social development. One of the main causes is the under-nutrition of infants due to under-nutrition of a mother during her pregnancy.
To focus and reduce the infant mortality rate in the country, the Indian government initiated many different campaigns. Realizing that a pregnant woman's health and diet has direct impact on the child's health, there was a need to to raise awareness about their health among general public. Hence this coin was released on the World Population Day (11th July,1996).
===XXX===
Bhagwan Mahavir: 2600th Janm Kalyanak - 2001

Year: 2001
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 9.07 gm
Diameter: 23.19 mm
Thickness: 2.77 mm
Commemorative issue: 2600th Anniversary of Birth of Bhagwan Mahavir.
Obverse: Asoka lion pedestal and the denomination below.
Reverse: The symbol of Jainism, the religion which follows principles of Bhagwan Mahavir.
Jainism is an Indian religion. It prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Bhagwan Mahavir was 24th, and the last Tirthankar("spiritual teacher") in Jainism. He was born in 599 B. C. at Kshatriyakunda (Bihar) to King Siddhartha and Queen Trishala. Though he was a prince, he left his home at the age of 30 to become an ascetic. He performed a severe penance for twelve and a half years and then in 558 B.C., he attained absolute enlightenment (a state of understanding ultimate truth). After this, he preached his first message for the attainment of selfpurification and selfperfection. The same path shown by him is followed today. In the year 527 B.C. Bhagwan Mahavir attained Nirvana.
On the occasion of 2600th birth anniversary of Bhagwan Mahavir, this 5 rupees coin was issued on the on 25th April, 2002. On this occasion another coin in the denomination of 100 rupees, was issued as proof/uncirculated coin.
 |
| Symbol of Jainism |
Details of the Symbol: It consists of Eight sided polygon, symbolizing the “Structure of Universe” On the top end of this universe structure, acrescent with a dot inside and 3 dots below, symbolizes the “Siddha Shila”, an abode of infinite Siddhas (meaning one who has achieved perfection ) is shown. Below the “Siddha Shila” the holiest “Swastika”symbol is shown. At the bottom a hand, with a wheel (Dharma Chakra) on the palm, with the word "Ahimsa" (meaning non-violence) in Devnagari is shown. It has the words “Parasparopagraho Jivanam”in Sanskrit (meaning All life is bound together by mutual support and interdependence).
Click here to know more about symbol of Jainism.
Click here to know more about Bhagwan Mahavir.
===XXX===
Dadabhai Naoroji - 2003

Year: 2003
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 9 gm
Diameter: 23 mm
Commemorative issue: Dadabhai Naoroji.
Obverse: Asoka lion pedestal and the denomination below.
Reverse: Bust of Naoroji.
 |
| Dadabhai Naoroji |
Dadabhai Naoroji (4 September 1825 – 30 June 1917), known as the Grand Old Man of India, was a Parsi intellectual, educator, cotton trader, and an early Indian political and social leader. He was a Member of Parliament (MP) in the United Kingdom House of Commons between 1892 and 1895, and the first Asian to be a British MP.
Naoroji is also credited with the founding of the Indian National Congress, along with A.O. Hume and Dinshaw Edulji Wacha. Naoroji was a mentor to both Gopala Krishna Gokhale and Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi. His book Poverty and Un-British Rule in India brought attention to the draining of India's wealth into Britain.
In commemoration of Dadabhai Naroji, India issued this 5 rupees commemorative coin on 2nd October, 2003, for general circulation.
Click here to know more about Dadabhai.
===XXX===
K. Kamraj - 2004

Year: 2004
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 8.9 gm
Diameter: 23.6 mm
Thickness: 2.9 mm
Commemorative issue: K. Kamaraj
Obverse: Asoka Lion pedestal and the denomination below.
Reverse: Bust of Kamaraj.
 |
| Kumarasami Kamraj |
Kumarasami Kamaraj better known as K. Kamaraj (15 July 1903 – 2 October 1975) was an Indian politician from Tamil Nadu widely acknowledged as the "Kingmaker" in Indian politics during the 1960s. He was the chief minister of Tamil Nadu during 1954-1963 and a Member of Parliament during 1952-1954 and 1969-1975. He was known for his simplicity and integrity.
He was involved in the Indian independence movement.[5] As a high-ranking office bearer of the Indian National Congress, he was instrumental in bringing to power two Prime Ministers, Lal Bahadur Shastri in 1964 and Indira Gandhi in 1966. In Tamil Nadu, his home state, he is still remembered for bringing school education to millions of the rural poor by introducing free education and the free Midday Meal Scheme during his tenure as chief minister. He was awarded India's highest civilian honour, the Bharat Ratna, posthumously in 1976.
In commemoration of K. Kamaraj, India issued this 5 rupees coin on 27th October 2004 for general circulation and 100 rupees coin as proof/uncirculated specimen.
Click here to know more about K. Kamraj.
===XXX===
Lal Bahadur Shastri Birth Centenary - 2004

Year: 2004
Metal: Stainless Steel
Weight: 6 gm
Diameter: 23 mm
Thickness: 2.19 mm
Commemorative issue: Birth Centennary of Lal Bahadur Shastri.
Obverse: Asoka lion pedestal and the denomination below.
Reverse: Bust of Shastri.
On the occasion of Lal Bahadur Shastri birth centenary celebrations, India issued this 5 rupees coin on 4th october, 2005, for general circulation.It was issued in 2 metal compositions i.e. Copper-Nickel and Stainless steel. Another coin in the denomination of 100 rupees was issued as proof/uncirculated specimen.
 |
| Lal Bahadur Shastri |
Lal Bahadur Shastri ( 2 October 1904, Mughalsarai – 11 January 1966, Tashkent) was the second Prime Minister of the Republic of India and a leader of the Indian National Congress party.
Shastri joined the Indian independence movement in the 1920s. Deeply impressed and influenced by Mahatma Gandhi, he became a loyal follower, first of Gandhi, and then of Jawaharlal Nehru. Following independence in 1947, he joined the latter's government and became one of Prime Minister Nehru's principal lieutenants, first as Railways Minister (1951–56), and then in a variety of other functions, including Home Minister. Shastri was chosen as Nehru's successor owing to his adherence of Nehruvian socialism after Nehru's daughter Indira Gandhi turned down Congress President K. Kamaraj's offer of premiership.
Shastri as Prime Minister continued Nehru's policies of non-alignment and socialism. He became a national hero following the Indo-Pakistan War of 1965. His slogan of "Jai Jawan Jai Kisan" ("Hail the soldier, Hail the farmer") became very popular during the war and is remembered even today.[2] The war was formally ended in the Tashkent Agreement of 10 January 1966; he died the following day mysteriously in Tashkent. It is said that he died of a heart attack.
Click here to know more about L.B. Shastri.
===XXX===
75 Years of Dandi March - 2005

Year: 2005
Metal: Copper-nickel
Weight: 8.85 gm
Diameter: 23 mm
Commemorative issue: 75th Anniversary Dandi March.
Obverse: Lion capitol of Ashoka Pillar and the value below.
Reverse: Gandhi leading marchers to Dandi.
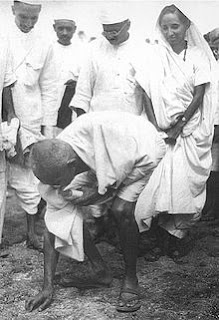 |
| Gandhi picking up a grain of salt at the end of Dandi march |
The Dandi March, also known as the Salt Satyagraha, began with the Dandi March on March 12, 1930, and was an important part of the Indian independence movement. It was a direct action campaign of tax resistance and nonviolent protest against the British salt monopoly in colonial India, and triggered the wider Civil Disobedience Movement. This was the most significant organized challenge to British authority since the Non-cooperation movement of 1920–22, and directly followed the Purna Swaraj declaration of independence by the Indian National Congress on January 26, 1930. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi i.e. Mahatma Gandhi led the Dandi march from his base, Sabarmati Ashram near Ahmedabad, to the sea coast near the village of Dandi. As he continued on this 24 day, 240 mile (390 km) march to produce salt without paying the tax, growing numbers of Indians joined him along the way. When Gandhi broke the salt laws at 6:30 am on April 6, 1930, it sparked large scale acts of civil disobedience against the British Raj salt laws by millions of Indians. The campaign had a significant effect on changing world and British attitude towards Indian independence and caused large numbers of Indians to join the fight for the first time.
In commemoration of the 75th anniversary of the Dandi March, India issued this 5 rupees commemorative coin on 2nd October, 2005 for general circulation and Another coin 100 Rupees as proof/uncirculated specimen.
Click here to know more about Dandi march.
===XXX===
Hello! Kindly tell me what the value of the coin is: Commemorative issue: 75th Anniversary Dandi March. Dated 1930 to 2005 in VF Condition. I cannot find it in the Krause Cat of coins.
ReplyDeleteThank you very much!
Hi David,
ReplyDeleteIn my opinion, Its worth of $1-$2.
dear sir
ReplyDeletei am latif from pondicherry i want to know how many kindes of five rupes are in the maricket if you know plz tell me that should be your most kindess '
my emil mirmirmir1975@yahoo.co.in
thanks
how much indra(hyd) and neru(hyd) 5 rupee coin?
ReplyDeletev.haja2006@yahoo.com
VERY INFORMATIVE AND ENJOYEABLE INFORMATION ABOUT Rs5 coins. congratulations. R. SOMVANSHI, Bareilly, UP
ReplyDeleteI know its too late but Thank you for your feedback, much appreciated!
Delete